5G era is coming! Now we all have a smartphone on our hands and you must have noticed the icon at the top of the screen (3G, 4G, Edge, LTE, etc.), showing you which type of network you are accessing. Now you may have heard that 5G is coming. But, do you have a clue what they mean? Please read on to find out some basics of 5G and more info you need to know.

1G, 2G, 2.5G, 2.75 G, 3G, 4G & 5G. What’s the Difference?
Simply put:
1G means the 1st generation of wireless cellular technology, 2G means the 2nd generation, and so forth.

- 1G – Voice Only
- 2G – SMS (Short Message Service) & MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service)
- 2.5G & 2.75G – Data
- 3G – More Data, Video Calling & Mobile Internet
- 4G – Faster Speed (Current Standard)
- 5G – Significantly Faster (The Coming Standard)
1G
In the 1980s, when cell phone technology was evolved from military use to consumer use, it began with the 1G standard, which supports only voice calls. The vague voice, short battery life as well as the insecurity of the 1G cell phone are inevitable.
Max speed of 1G: 2.4 Kbps
2G
1G (analog) to 2G (digital) evolution took 20 years, turning a mono-service to multi-service, which happened in Finland, 1991. 2G provided narrowband internet service and introduced many fundamental services that still play a part in our current lives like SMS (Short Message Service), MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service), internal roaming, conference calls, etc.
Max speed of 2G GPRS: 50 Kbps
Max speed of 2G EDGE: 1 Mbps
2.5G and 2.75G
You may not have heard of 2.5G and 2.75G, but they did exist as informal standards. They were invented for marketing purposes, bridging the gap between 2G and 3G to make slow data transmission possible. 2.5G refers to the 2G standard combined with GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) or other services that cannot be found in 1G/2G network; 2.75G refers to EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution) Networks.
Max speed of 2.5G GPRS: 57.6 Kbps
Max speed of 2.75G EDGE: 238.8 kbps
3G
3G introduced in 1998 set the standards for many wireless technologies we have today, like web browsing, multimedia streaming, email, image sharing, etc. “mobile broadband”, as a term, was applied to 3G. Then, as informal standards, 3.5G & 3.75G were introduced, with much faster speed and more features.
Max speed of 3G: 2 Mbps for non-moving devices while 384 Kbps for portable devices
4G
The current stand, 4G, was introduced in 2008. 4G supports 3G and 2G networks while adding more services like video conference, gaming, HD mobile TV, 3D TV and some other features that require higher speed. Most smartphone models are compatible with both 3G & 4G networks. However, while the major big cities in the world have been covered by 4G network, some cities in even the most advanced countries are not even 3G-covered at present due to regionally unbalanced development.
Max speed of 4G: 1 Gbps for non-moving devices while 100 Mbps for portable devices
5G
5G is under development but luckily, a few companies have released their 5G handsets. AT&T has come out with their 5G plans. The one-off roll-out cost will be $500 while AT&T will charge $70/month for 15GB on the new 5G hotspot. Still, a lot of money to get started. 5G provides incredibly faster speed.
Max speed of 5G: 35.46 Gbps
5G Key Features
Now we all know that 5G is faster, but 5G means more than speed. It is so far the most robust wireless technologies that people have seen. Its powerful network will show a huge impact on the way we live, work and entertain ourselves.
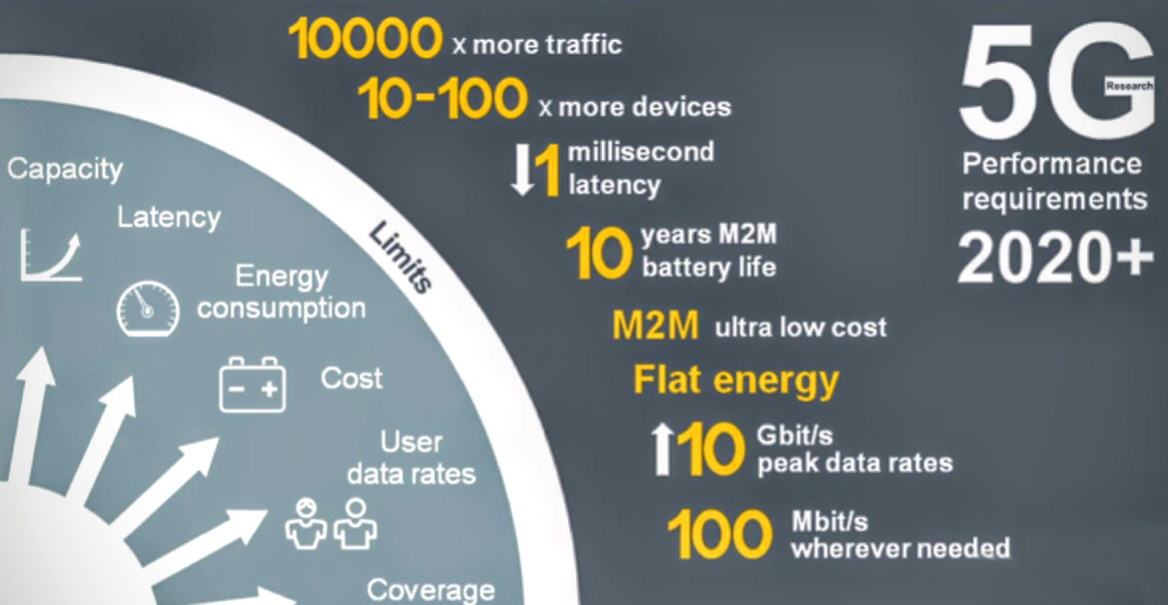
Faster Speed
5G was born faster than its preceding generations – 5G can provide speed as fast as 35.46 Gbps, which means that, ideally, you can download a full HD movie within several seconds via 5G network, while it may take more than 10 minutes via 4G.
Lower Latency
5G’s low latency will help support communication, reducing delay & lags while we are using cell phones, self-driving cars and so on. 4G’s latency is somewhere between 15 to 60 milliseconds, which is too much for communication between autonomous vehicles, Xbox Live online gaming and other activities that require higher network speed. 5G’s latency is expected to be as low as unnoticeably 1 or 2 milliseconds – that’s basically 0 for human users.
Greater Capacity
5G’s capacity will enable more and more smart gadgets to utilize the network, changing our lives. Home appliances, online surveillance cameras, smart locks and a number of Internet of Things (IoT) as well as VR devices and UHD video streaming can be working at the same network system while the 4G network would not be able to fit the needs of the average users.
Strict Stability
5G network is far more stable than 4G, which means fewer dropped/missed internet calls or disconnections. It is crucial, and sometimes even life-saving like when it’s used in self-driving cars and for medical purposes.
Better Flexibility
Network slicing, a fundamental 5G technology to make 5G system flexible. 5G can be tailored to the needs of any specific services, which will add more efficiency and agility to network operations.
Longer Battery Life
Despite its extremely high speed, 5G is actually battery-saving. Instead of draining your battery like a slurpy, 5G can make month-long battery life possible.
How Can Business Benefit from 5G
5G revolution is a game changer to bring new benefits to businesses of all sizes. Based on a recent research, the rise and spreading of 5G will support over various industries of worth of over $12 trillion., including the products and services of entertainment, education, insurance, healthcare, transportation, delivery, etc. Approximately, 22 million jobs will be created by 5G value chain in next decade.

Productivity

5G network will help business to work effectively, leading to more savings and more revenue. The productivity will emerge rapidly due to the bursting efficiency.
Competition

Along with the flourish of 5G network and the boost of productivity, small business will grow faster than ever before in history, which will bring more global competition.
Remote Working

Remote working is evolving, but it is not as conducive to productivity as people expected or as it should be due to cultural and technical issues in business. With 5G’s seamless connectivity, low latency, high resolution and realistic audio, at least there will be fewer awkwardness for telepresence like remote meetings.
Rural Innovation

Many people countries and urban areas are waiting for 5G to grow businesses and seizing opportunities from home. By 2017, only 77.28% of the UK has 4G coverage, United States 90.32%, France 68.31%, etc. However, a few areas don’t even have 3G covered, e.g., a French vice mayor made a Christmas wish to Santa Claus lately asking for 3G. The governments, private sector, as well as academia will be exploring rural business possibilities and opportunities brought up by 5G, including agriculture, utilities, tourism, etc.
Private Network for Businesses
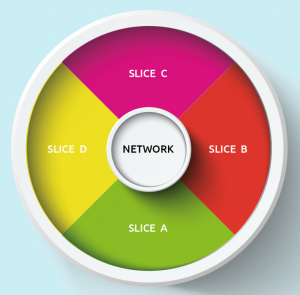
Network slicing enables businesses to tailor network to their circumstances, creating practical and private 5G network based on specific requirements. Thus the 5G can assign the resources intelligently for different purposes.
Low Cost

Eventually, 5G will be cheaper than 4G – it may take some time, but it will happen. 5G is software-based, which does not require cables or other physical materials, leading to fewer overheads for mobile operators. The savings can be partially turned into business customer benefits.
Ease on Commutes

5G’s fast and undelayed network, automated transport, personal or public, can be smarter, safer and easier than ever. Both employers & employees will save time from commuting & business travels.
